डायबिटिक नेफ्रोपैथी क्या है?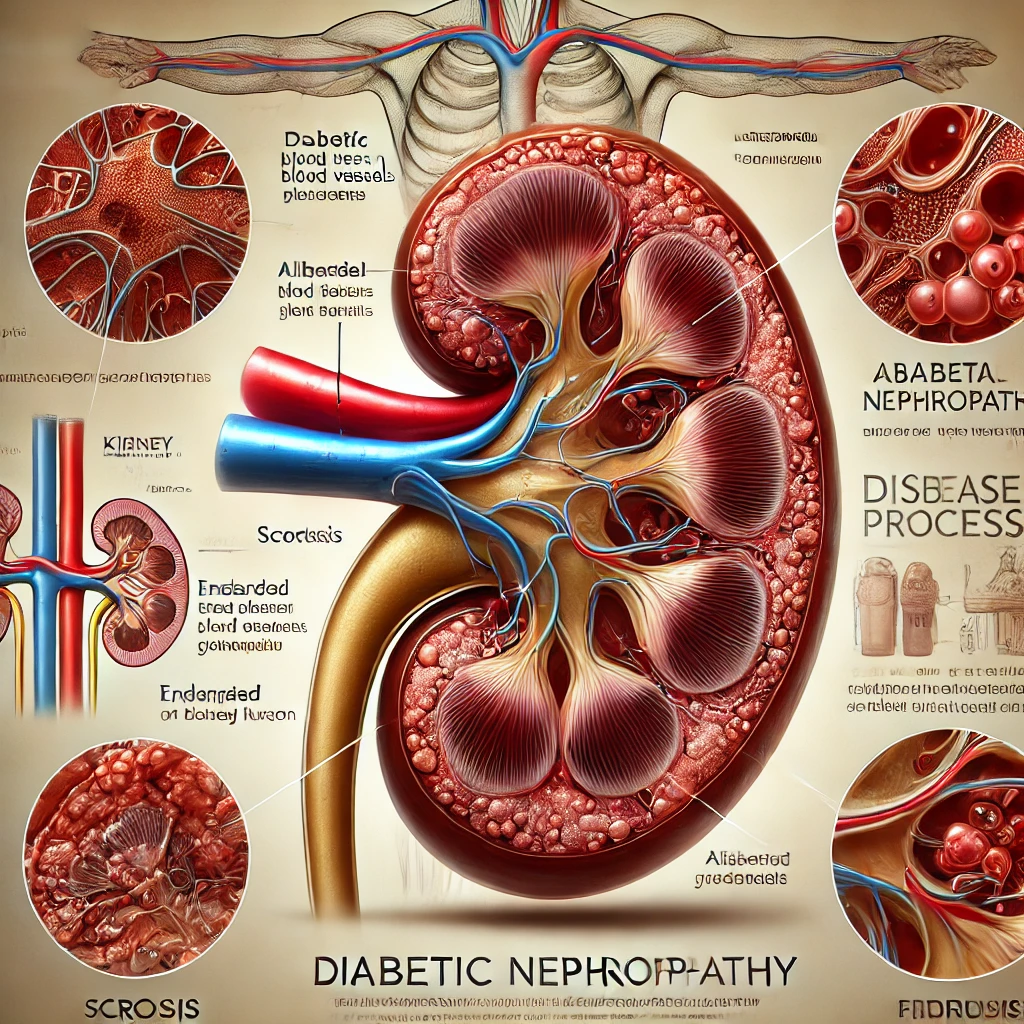
डायबिटिक नेफ्रोपैथी एक किडनी की बीमारी है जो मधुमेह के कारण होती है। यह तब होती है जब लंबे समय तक उच्च रक्त शर्करा किडनी की छोटी रक्त वाहिकाओं (ग्लोमेरुली) को नुकसान पहुंचाती है, जिससे किडनी की कार्यक्षमता में कमी आती है। समय के साथ, यह क्षति किडनी फेलियर का कारण बन सकती है, जो जीवन के लिए खतरा बन सकती है और डायलिसिस या किडनी ट्रांसप्लांट की आवश्यकता पैदा कर सकती है।
किडनी क्षति में उच्च रक्त शर्करा और उच्च रक्तचाप की भूमिका
डायबिटिक नेफ्रोपैथी में मुख्य योगदान देने वाले कारक लगातार उच्च रक्त शर्करा स्तर और अनियंत्रित उच्च रक्तचाप (हाइपरटेंशन) हैं।
उच्च रक्त शर्करा (हाइपरग्लाइसीमिया): जब रक्त शर्करा स्तर लंबे समय तक ऊंचा रहता है, तो अतिरिक्त ग्लूकोज किडनी की नाजुक रक्त वाहिकाओं (ग्लोमेरुली) को नुकसान पहुंचा सकता है। ये रक्त वाहिकाएं रक्त से अपशिष्ट को फ़िल्टर करने के लिए आवश्यक होती हैं। समय के साथ, यह क्षति किडनी की फ़िल्टरिंग क्षमता को कम कर देती है, जिससे प्रोटीन का रिसाव (एल्ब्यूमिन्यूरिया) होता है और किडनी के ऊतकों को और अधिक नुकसान पहुंचता है।
उच्च रक्तचाप (हाइपरटेंशन): अनियंत्रित उच्च रक्तचाप भी किडनी की रक्त वाहिकाओं पर अतिरिक्त दबाव डालता है। यह दबाव समय के साथ रक्त वाहिकाओं को कठोर और संकुचित कर सकता है, जिससे रक्त प्रवाह कम हो जाता है।
अनुवांशिक प्रवृत्ति और जीवनशैली के प्रभाव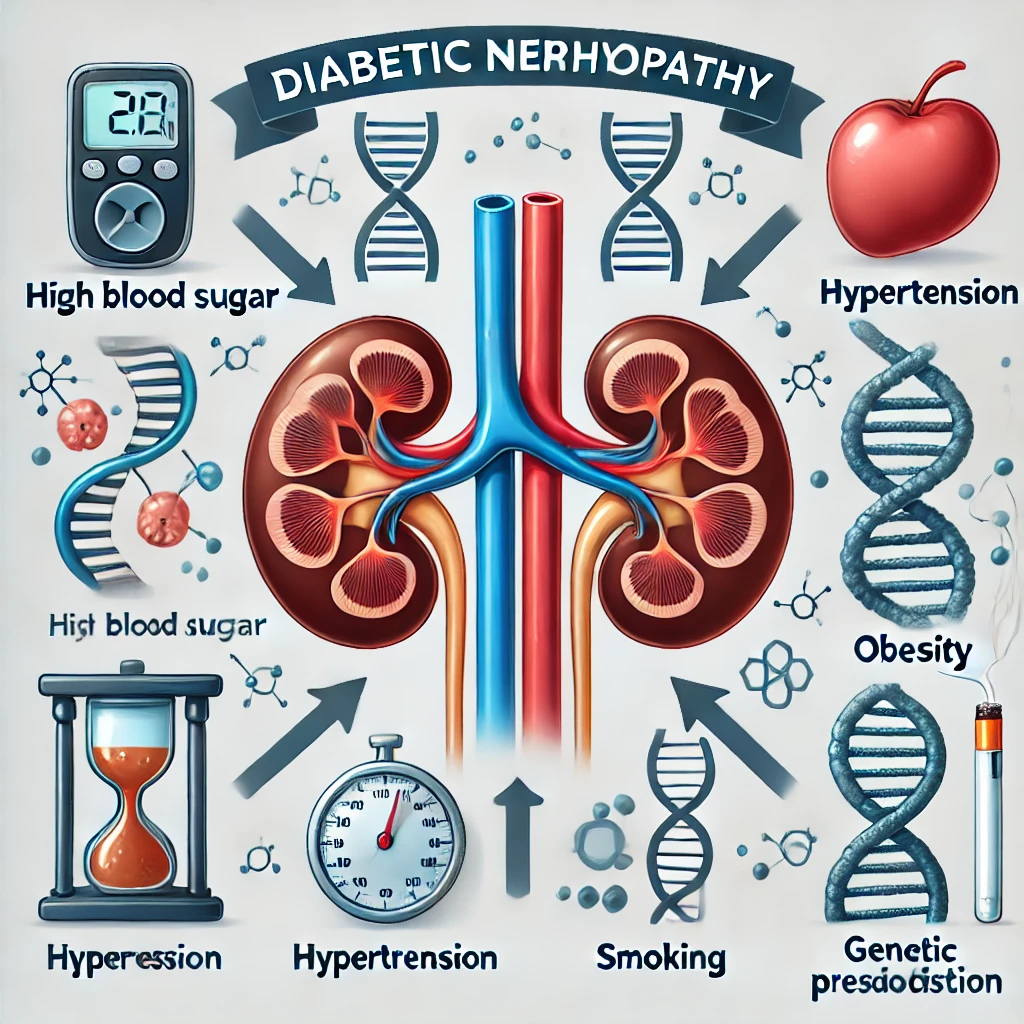
जहां मधुमेह और उच्च रक्तचाप डायबिटिक नेफ्रोपैथी में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाते हैं, वहीं अनुवांशिक कारक और जीवनशैली के विकल्प भी जोखिम को काफी प्रभावित करते हैं।
अनुवांशिक कारक: कुछ व्यक्तियों में आनुवंशिक प्रवृत्ति होती है, जो उन्हें किडनी क्षति के प्रति अधिक संवेदनशील बनाती है। यदि परिवार में मधुमेह या किडनी रोग का इतिहास है, तो डायबिटिक नेफ्रोपैथी विकसित होने की संभावना बढ़ जाती है।
जीवनशैली विकल्प: निष्क्रिय जीवनशैली, अस्वास्थ्यकर खानपान की आदतें और अपर्याप्त शारीरिक गतिविधि न केवल मधुमेह और उच्च रक्तचाप को बढ़ावा देती हैं, बल्कि किडनी रोग के जोखिम को भी बढ़ाती हैं। संतुलित आहार का पालन न करना और व्यायाम की कमी से शरीर में रक्त शर्करा और रक्तचाप का स्तर बढ़ सकता है, जो किडनी को नुकसान पहुंचाने वाले प्रमुख कारक हैं।
अतिरिक्त जोखिम कारक
डायबिटिक नेफ्रोपैथी विकसित होने की संभावना को प्रभावित करने वाले कई कारक हैं, जिनमें से कुछ को बदला जा सकता है और कुछ को नहीं।
मोटापा: अधिक वजन या मोटापा टाइप 2 मधुमेह और उच्च रक्तचाप के विकास की संभावना को बढ़ा देता है, जो सीधे किडनी को नुकसान पहुंचा सकते हैं। मोटापा शरीर पर अतिरिक्त तनाव डालता है और इंसुलिन प्रतिरोध को बढ़ाता है, जिससे किडनी पर अधिक दबाव पड़ता है।
धूम्रपान: धूम्रपान किडनी रोग की प्रगति को तेज कर सकता है। यह किडनी तक रक्त प्रवाह को सीमित करता है, ऑक्सीडेटिव तनाव को बढ़ाता है और शरीर में सूजन को बढ़ा सकता है। धूम्रपान छोड़ने से किडनी की कार्यक्षमता में गिरावट की गति को धीमा करने में मदद मिल सकती है।
खराब मधुमेह प्रबंधन: यदि रक्त शर्करा के स्तर की नियमित निगरानी नहीं की जाती, दवाओं को समय पर नहीं लिया जाता, या नियमित स्वास्थ्य जांच नहीं कराई जाती, तो यह स्थिति और भी गंभीर हो सकती है।
मधुमेह की अवधि: मधुमेह की अवधि जितनी लंबी होती है, व्यक्ति के किडनी क्षति का जोखिम उतना ही बढ़ता है। लंबे समय तक उच्च रक्त शर्करा का प्रभाव धीरे-धीरे किडनी की कार्यक्षमता को प्रभावित करता है और नेफ्रोपैथी की संभावना में वृद्धि होती है।
आयु और जातीयता: बड़ी उम्र के व्यक्तियों और कुछ विशेष जातीय समूहों जैसे अफ्रीकी-अमेरिकी, हिस्पैनिक और मूल अमेरिकी लोगों में डायबिटिक नेफ्रोपैथी का जोखिम अधिक होता है। यह जोखिम आनुवंशिक और सामाजिक-आर्थिक कारकों के संयोजन के कारण बढ़ता है।
महत्वपूर्ण लक्षण
पेशाब में प्रोटीन (एल्ब्यूमिन) का रिसाव: पेशाब में झाग आना एक संकेत हो सकता है। सूजन (एडेमा):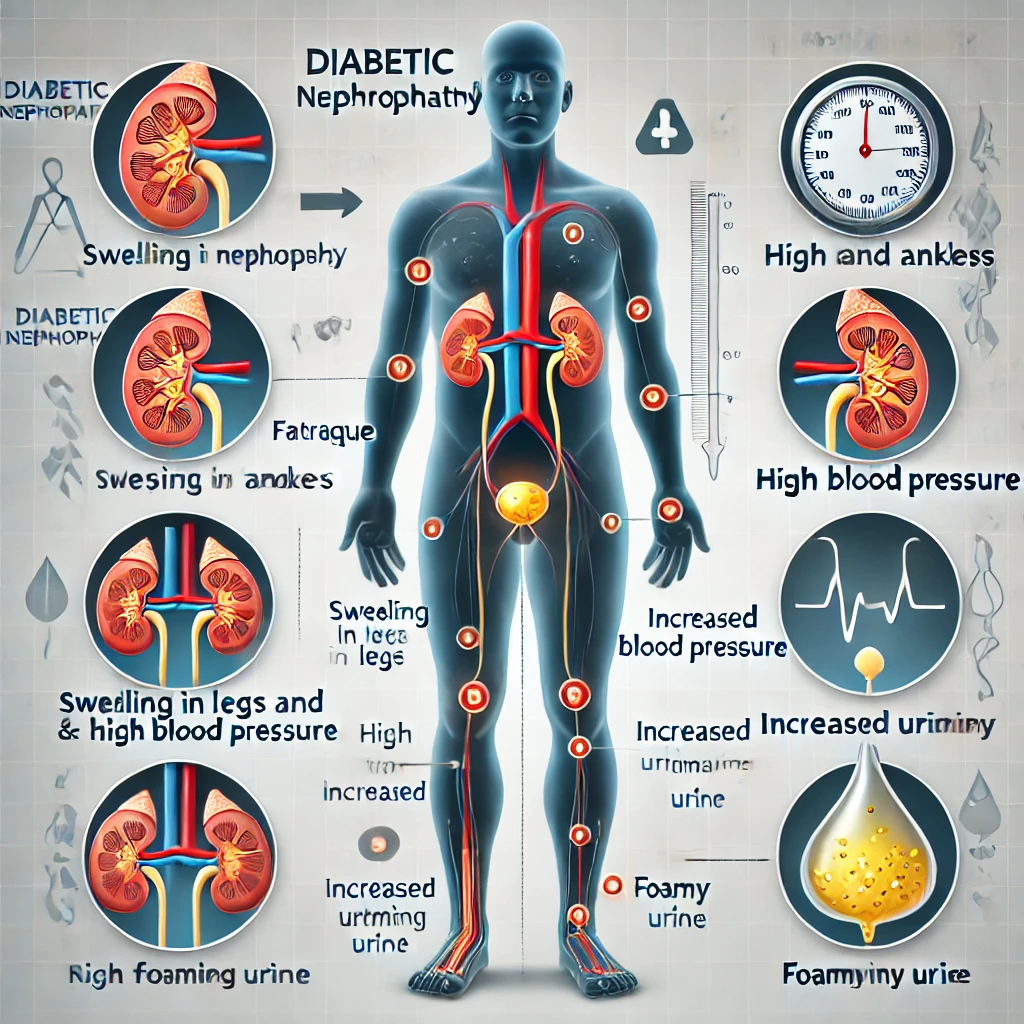 पैरों, टखनों, चेहरे या हाथों में सूजन।
पैरों, टखनों, चेहरे या हाथों में सूजन।
रक्तचाप में वृद्धि: उच्च रक्तचाप किडनी क्षति का एक सामान्य संकेत है। थकान और कमजोरी: किडनी की कार्यक्षमता कम होने पर शरीर में अपशिष्ट पदार्थ जमा हो सकते हैं।
भूख में कमी और मतली: शरीर में विषाक्त पदार्थों का निर्माण इन लक्षणों का कारण बन सकता है। महत्व: लक्षणों की शीघ्र पहचान और समय पर हस्तक्षेप किडनी की कार्यक्षमता को बनाए रखने और नेफ्रोपैथी की प्रगति को धीमा करने में मदद कर सकते हैं। नियमित जांच और चिकित्सा परामर्श अत्यंत आवश्यक है।
सांस लेने में कठिनाई: जब शरीर में अतिरिक्त तरल जमा होता है, खासकर फेफड़ों में, तो इससे सांस लेने में परेशानी हो सकती है। यह स्थिति अक्सर एडिमा (सूजन) से जुड़ी होती है और किडनी की खराब कार्यप्रणाली का संकेत देती है।
लगातार खुजली: रक्त में अपशिष्ट पदार्थों के बढ़ने से त्वचा में जलन और लगातार खुजली हो सकती है। यह यूरीमिक टॉक्सिन्स (विषैले पदार्थों) के त्वचा पर प्रभाव के कारण होता है।
लक्षणों की पहचान करना और समय पर उपचार शुरू करना किडनी क्षति को धीमा करने और जीवन की गुणवत्ता में सुधार करने में मदद कर सकता है। नियमित स्वास्थ्य जांच और लक्षणों पर ध्यान देना बहुत जरूरी है।
नियमित स्क्रीनिंग का महत्व
डायबिटिक नेफ्रोपैथी अक्सर बिना किसी स्पष्ट लक्षण के विकसित हो सकती है, इसलिए समय पर पहचान के लिए नियमित किडनी फंक्शन टेस्ट करना आवश्यक है।
प्रमुख परीक्षण
मूत्र परीक्षण: यह परीक्षण मूत्र में प्रोटीन (एल्ब्यूमिन) की उपस्थिति की जांच करता है। यदि एल्ब्यूमिन का रिसाव होता है, तो यह किडनी क्षति का पहला संकेत हो सकता है।
रक्त परीक्षण: इसमें क्रिएटिनिन के स्तर की जांच करके ग्लोमेरुलर फिल्ट्रेशन रेट (GFR) का अनुमान लगाया जाता है, जो किडनी की कार्यक्षमता को दर्शाता है। GFR में कमी किडनी की कार्यक्षमता में गिरावट का संकेत देती है।
रक्तचाप की निगरानी: उच्च रक्तचाप अक्सर किडनी की कार्यक्षमता में कमी से जुड़ा होता है। इसलिए, नियमित रूप से रक्तचाप की जांच करना महत्वपूर्ण है।
डायबिटिक नेफ्रोपैथी के शुरुआती लक्षण अक्सर अनदेखे रह जाते हैं, इसलिए मधुमेह से ग्रसित लोगों के लिए सक्रिय रूप से स्क्रीनिंग कराना बहुत जरूरी है। यदि इस स्थिति का समय पर पता लगाया जाए, तो रक्त शर्करा और रक्तचाप को सही तरीके से प्रबंधित करके किडनी को होने वाले नुकसान को धीमा या रोका जा सकता है। इसके साथ ही, जीवनशैली में सुधार और चिकित्सा उपचार भी मददगार साबित होते हैं। जागरूक और सतर्क रहकर, मधुमेह से पीड़ित व्यक्ति अपनी किडनी की सेहत पर नियंत्रण रख सकते हैं और उन्नत डायबिटिक नेफ्रोपैथी से जुड़ी गंभीर जटिलताओं से बच सकते हैं।

 complication that arises from diabetes and affects the kidneys. It happens when consistently high blood sugar levels cause damage to the small blood vessels (glomeruli) in the kidneys, which hinders their ability to filter out waste, toxins, and excess fluids from the bloodstream. If this damage continues over time, it can result in chronic kidney disease (CKD) and, in severe instances, kidney failure, which may necessitate dialysis or a kidney transplant.
complication that arises from diabetes and affects the kidneys. It happens when consistently high blood sugar levels cause damage to the small blood vessels (glomeruli) in the kidneys, which hinders their ability to filter out waste, toxins, and excess fluids from the bloodstream. If this damage continues over time, it can result in chronic kidney disease (CKD) and, in severe instances, kidney failure, which may necessitate dialysis or a kidney transplant.